Understanding the Essentials of Superior Steel Protection
The world of industrial materials relies heavily on galvanized steel coating to provide lasting protection against corrosion and environmental damage. This protective layer serves as a crucial barrier that determines the longevity and performance of steel structures across various applications. From construction projects to manufacturing processes, the quality of galvanized steel coating plays a pivotal role in ensuring durability and cost-effectiveness.
Professionals in the manufacturing and construction industries understand that not all galvanized coatings are created equal. The distinction between high-quality and subpar coating can mean the difference between decades of reliable service and premature failure. This comprehensive guide will explore the key indicators and methods to identify superior galvanized steel coating, ensuring you make informed decisions for your projects.

Visual Assessment Techniques
Surface Appearance and Uniformity
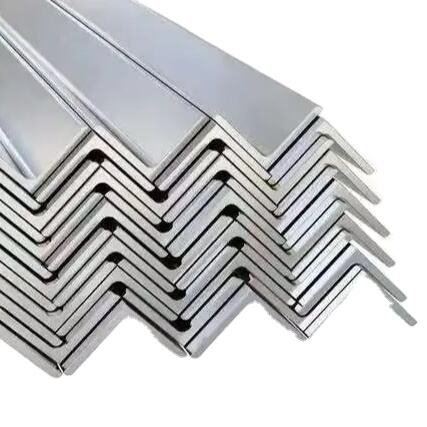
A high-quality galvanized steel coating exhibits specific visual characteristics that trained eyes can identify. The surface should display a uniform, bright spangled finish, which is characteristic of properly galvanized steel. This distinctive crystalline pattern, often described as a flower-like or snowflake appearance, indicates optimal zinc coating adhesion and proper cooling conditions during the galvanization process.
Look for consistency in the coating's appearance across the entire surface. Quality galvanized steel coating should be free from bare spots, blisters, or rough areas. The finish should appear smooth and continuous, though some variation in the spangle pattern is normal and doesn't necessarily indicate poor quality.
Thickness Distribution Analysis
The thickness of galvanized steel coating is crucial for long-term protection. Professional coating inspectors use magnetic thickness gauges to measure coating thickness at various points across the surface. A high-quality coating will show consistent thickness readings within acceptable tolerance ranges, typically specified by industry standards such as ASTM A123.
Areas of particular importance include edges, corners, and welded joints, where coating thickness can vary. These zones require special attention during inspection as they are often the first points of failure in substandard galvanized coatings.
Physical Testing Methods
Adhesion Testing Procedures
The bond between the galvanized steel coating and the base metal is fundamental to its protective capabilities. Industry-standard adhesion tests, such as the knife test or bend test, help verify the coating's integrity. Quality galvanized coatings should resist flaking, peeling, or separation from the steel substrate when subjected to these standardized tests.
Modern coating facilities employ sophisticated testing equipment to ensure their galvanized steel coating meets or exceeds industry specifications. These tests simulate real-world conditions and stress factors that the coating might encounter during its service life.
Chemical Composition Verification
The chemical makeup of galvanized steel coating significantly influences its performance. Professional laboratories can conduct spectrographic analysis to determine the exact zinc content and identify any additional alloying elements present in the coating. High-quality coatings typically contain specific percentages of aluminum and other elements that enhance corrosion resistance and coating durability.
Regular chemical analysis helps maintain consistency in coating quality and ensures compliance with international standards. This verification process is particularly important for applications where coating performance is critical to safety and longevity.
Environmental Performance Indicators
Corrosion Resistance Standards
Superior galvanized steel coating demonstrates exceptional resistance to various environmental conditions. Salt spray testing, humidity chamber exposure, and weathering trials provide valuable data about coating performance. Quality coatings should show minimal signs of white rust or red rust after extended exposure to harsh conditions.
Industry standards specify minimum performance requirements for different environmental exposure levels. High-quality coatings often exceed these baseline requirements, offering enhanced protection in aggressive environments such as coastal areas or industrial zones.
Durability Under Extreme Conditions
The true test of galvanized steel coating quality lies in its performance under challenging conditions. Temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress can all impact coating integrity. Premium galvanized coatings maintain their protective properties even when subjected to these extreme conditions.
Long-term exposure studies have shown that properly applied, high-quality galvanized coatings can provide effective protection for 50 years or more in moderate environments, and 20-25 years in severe environments. This exceptional durability makes quality coating essential for critical infrastructure and long-term installations.
Quality Control Documentation
Certification Requirements
Reputable manufacturers maintain detailed documentation of their galvanized steel coating processes and quality control measures. This documentation includes coating thickness measurements, test results, and compliance certificates. Quality coatings should be accompanied by comprehensive certification packages that verify adherence to relevant industry standards.
Important documentation elements include batch testing reports, material certificates, and process control records. These documents provide traceability and assurance of coating quality, essential for critical applications and regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing Process Controls
The consistency and reliability of galvanized steel coating depend heavily on strict process controls during manufacturing. Leading coating facilities implement sophisticated monitoring systems to maintain optimal conditions throughout the galvanizing process. Parameters such as zinc bath temperature, immersion time, and cooling rates are carefully controlled to ensure coating quality.
Regular calibration of equipment, maintenance of bath chemistry, and operator training programs are integral components of quality coating production. These controls help prevent common defects and ensure consistent coating performance across production runs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the optimal thickness for galvanized steel coating?
The optimal thickness of galvanized steel coating depends on the specific application and environmental conditions. Generally, for structural steel applications, a coating thickness of 3.5 to 5 mils (85-125 micrometers) is considered standard. However, more severe environments may require thicker coatings up to 7 mils (175 micrometers) or more for maximum protection.
How long does high-quality galvanized steel coating last?
High-quality galvanized steel coating typically provides protection for 50-75 years in rural environments, 20-35 years in urban/suburban settings, and 10-25 years in severe marine or industrial environments. The actual lifespan depends on environmental factors, coating thickness, and proper maintenance practices.
Can damaged galvanized steel coating be repaired?
Yes, damaged galvanized steel coating can be repaired using zinc-rich paints or spray galvanizing compounds. However, these repairs may not provide the same level of protection as the original hot-dip galvanized coating. For critical applications, it's often better to replace severely damaged components rather than attempt repairs.